Silicon bronze welding minimizes heat-affected zones (HAZ) in metal fabrication, especially automotive body work, by leveraging its copper-tin-silicon alloy for exceptional heat resistance. This technique reduces structural weaknesses and improves aesthetic quality, making it ideal for intricate components requiring strength under varying temperatures compared to traditional methods. Precise control of welding parameters and specialized techniques like preheating further mitigate HAZ effects in applications like collision repair and paintless dent removal.
Silicon bronze welding is a game-changer when it comes to minimizing heat-affected zones (HAZ), a critical aspect of the welding process. This article delves into the science behind HAZ, exploring why they occur and their potential impact on materials. We then highlight the unique advantages of silicon bronze as a weld metal, showcasing its superior resistance to thermal distortion. Finally, we offer practical techniques to effectively minimize HAZ during silicon bronze welding, ensuring high-quality, durable results.
- Understanding Heat-Affected Zones in Welding
- Advantages of Silicon Bronze for Reduced HAZ
- Techniques to Minimize Heat-Affected Zones Effectively
Understanding Heat-Affected Zones in Welding

In the world of metal fabrication, especially in tasks like car collision repair and automotive body work, understanding heat-affected zones (HAZ) is crucial for ensuring structural integrity and quality in auto repair services. HAZ refers to the area around a weld joint that’s subjected to elevated temperatures during the welding process. This region experiences changes in mechanical properties due to heat input, which can lead to weaknesses or vulnerabilities in the final product. In traditional welding methods, these zones might be a concern for long-term durability, particularly in sensitive applications like automotive engineering.
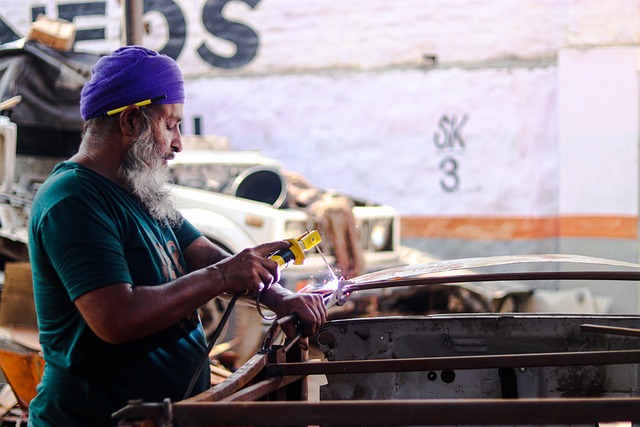
Silicon bronze welding emerges as a game-changer in mitigating HAZ. This specialized technique incorporates silicon into the weld metal, creating an alloy that possesses exceptional heat resistance and thermal stability. By using silicon bronze welding in car collision repair and automotive body work, technicians can minimize the size and impact of HAZ, ensuring the structural soundness of vehicles over time. This is particularly beneficial for intricate vehicle components where maintaining strength and integrity under varying temperatures is paramount.
Advantages of Silicon Bronze for Reduced HAZ

Silicon bronze welding offers significant advantages when it comes to minimizing heat-affected zones (HAZ) in metal fabrication. This unique alloy, composed of copper, tin, and silicon, exhibits excellent thermal properties that make it ideal for applications requiring precise control over heat input. Silicon bronze’s ability to withstand high temperatures without undergoing significant degradation ensures that the surrounding material remains intact, reducing the likelihood of HAZ formation.
In comparison to traditional welding techniques, silicon bronze welding can be particularly beneficial in delicate fabrication processes, such as those involved in collision center and Mercedes-Benz repair, where preserving structural integrity is paramount. The low thermal conductivity of silicon bronze allows for a more localized heat input, minimizing the impact on adjacent materials. This precision not only reduces HAZ but also facilitates cleaner, stronger welds, making it an attractive choice for professional bumper repair and other intricate metalworking tasks.
Techniques to Minimize Heat-Affected Zones Effectively

Minimizing heat-affected zones (HAZ) during silicon bronze welding is a critical aspect of ensuring structural integrity and aesthetic quality in various applications, including automotive repair services and collision repair. One effective technique involves precise control of welding parameters such as voltage, current, and speed. By carefully adjusting these settings, welders can reduce the size and impact of HAZ, minimizing potential weakness and warping.
Additionally, utilizing specialized techniques like preheating and post-welding heat treatment can significantly mitigate HAZ effects. Preheating the workpiece before welding prepares it for the thermal stress, while controlled cooling after welding helps to stabilize the metal, further reducing the size and severity of HAZ. These methods are particularly valuable in paintless dent repair processes, where maintaining the original finish without affecting surrounding areas is paramount.
Silicon bronze welding offers a powerful solution to mitigate heat-affected zones (HAZ), a critical consideration in ensuring structural integrity and long-term performance of welded components. By leveraging the unique properties of silicon bronze, such as its excellent thermal conductivity and ability to form strong, durable bonds, welders can achieve cleaner, more precise results with reduced HAZ. Combining these advantages with effective techniques, like controlled heat input and optimized cooling rates, allows for minimizing the impact of heat on surrounding materials, making silicon bronze welding a reliable and efficient choice for various industrial applications.